Managing High Cholesterol: When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough

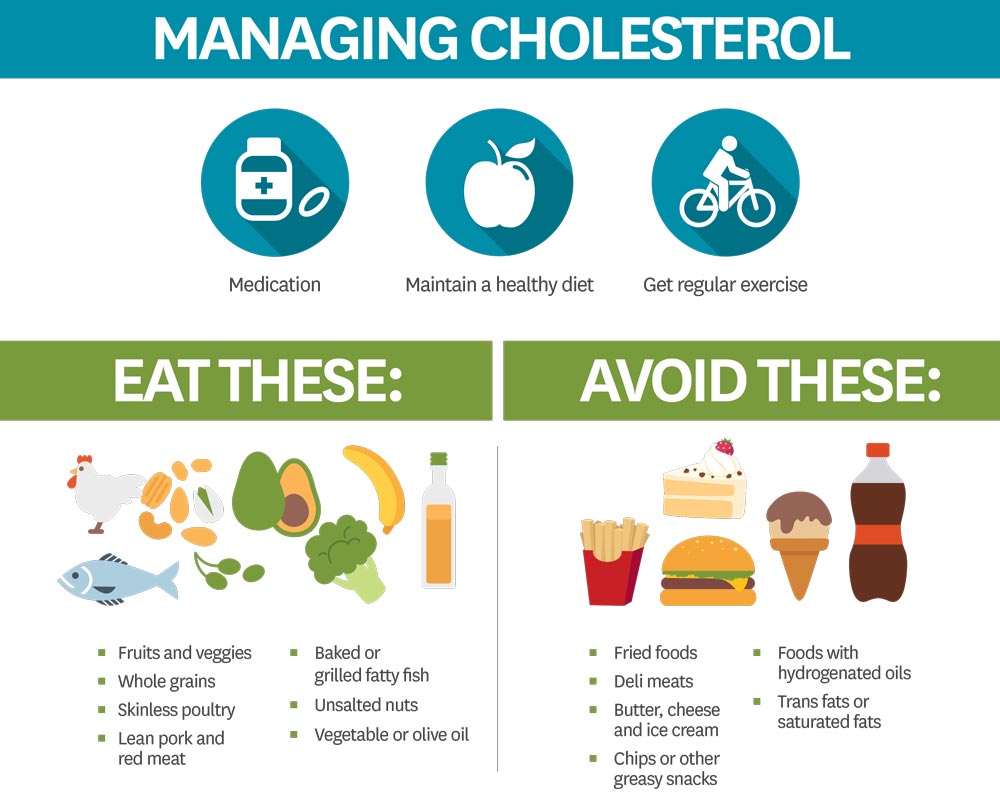
High cholesterol is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, but managing it isn’t always as simple as eating a healthy diet and exercising. While lifestyle changes can help, some people may need medication to manage their cholesterol effectively. Here’s a look at when medication might be necessary, along with common treatments and their benefits.
Do Diet and Exercise Help Enough?

Your cholesterol levels are made up of:
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Known as the “good” cholesterol.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): The “bad” cholesterol that can build up in your arteries.
- Non-HDL Cholesterol: This is a calculation of all the bad types of cholesterol combined.
A lipid panel is the test used to check these levels, including triglycerides, another type of fat in the blood. If you have high cholesterol, it means you have too much LDL or non-HDL cholesterol, which increases your risk for heart disease and stroke.
For many, diet and exercise can help manage high cholesterol. Regular physical activity and a healthy diet can help lower LDL levels while raising HDL levels. However, some people might need medication if lifestyle changes aren’t enough. This is especially true for those with a family history of high cholesterol or those already at higher risk for heart disease.
When Is Medication Needed for High Cholesterol?

There are certain situations when doctors may recommend medication to manage high cholesterol:
- High Risk for Heart Disease: If your cholesterol levels are high enough to significantly increase your risk of heart disease (or you’ve already had a heart attack or stroke), medications are often recommended.
- LDL Higher Than 190 mg/dL: If your LDL level is greater than 190 mg/dL, medication is likely necessary to lower it.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk for heart disease, so cholesterol medication may be needed even if LDL isn’t very high.
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD): If you have a history of heart attack, angina, or blocked arteries, medication will likely be required to reduce the risk of another event.
- Triglyceride Levels Over 200 mg/dL: High triglycerides increase your risk for heart disease. If your triglyceride level exceeds 500 mg/dL, your doctor will prescribe medication due to the risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score: Doctors use a risk score to determine your chance of having a heart attack or stroke in the next 10 years. If the score is over 5%, medication may be recommended.
Common Cholesterol Medications

- Statins: These are the most commonly prescribed drugs to lower LDL cholesterol. They work by blocking the enzyme your liver uses to make cholesterol. Statins are typically prescribed if you have high cholesterol levels or are at risk for heart disease.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: A newer class of drugs that block a protein called PCSK9, which allows the liver to remove more LDL from the bloodstream. These are typically used if statins aren’t effective on their own. Alirocumab (Praluent) and Evolocumab (Repatha) are common examples.
- siRNA (Small Interfering RNA): Medications like Leqvio (Inclisiran) lower cholesterol by interfering with PCSK9, reducing LDL levels. It’s administered as a biannual injection.
- Other Medications: If statins aren’t suitable, doctors may prescribe fibrates, niacin, bile acid sequestrants, or cholesterol absorption inhibitors like Ezetimibe.
Are These Medications Safe?

Yes, most cholesterol medications are generally safe, though side effects can occur. Statins, for instance, can cause muscle aches or liver problems. If you experience side effects, your doctor may adjust your dose or switch you to a different medication. In some cases, statins may also increase blood sugar levels, which is important to monitor, especially for people with diabetes.
Do I Need to Stay on Cholesterol Medication Forever?
This depends on your personal health and the severity of your cholesterol issues. Some people can successfully lower their cholesterol through diet, exercise, and weight management and can eventually stop taking cholesterol medications. However, people with a strong family history of high cholesterol or those at high risk for heart disease might need to stay on medication long-term.
Even if you’re on medication, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial. This means:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet (high in fiber, low in saturated fats)
- Getting regular exercise (at least 150 minutes per week)
- Avoiding smoking
- Limiting alcohol intake
How Can I Lower My Cholesterol Naturally?

Alongside medications, here are some simple, effective ways to naturally reduce cholesterol:
- Increase fiber: High-fiber foods such as oats, beans, lentils, and fruits can help lower cholesterol.
- Avoid saturated fats: Cut back on red meat and full-fat dairy products.
- Exercise: Physical activity can help raise HDL (good cholesterol) and lower LDL (bad cholesterol).
- Avoid smoking: Smoking lowers your good cholesterol, making it harder to fight off heart disease.
- Limit alcohol: Excessive drinking can raise blood pressure and triglycerides.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can cholesterol medications cure high cholesterol?
No, cholesterol medications help control cholesterol levels, but lifestyle changes (like diet and exercise) are still crucial for long-term management.
2. How do I know if I need cholesterol medication?
Your doctor will assess your cholesterol levels, risk factors, and cardiovascular risk score to determine whether medication is necessary.
3. Can cholesterol medication cause side effects?
Some cholesterol medications, especially statins, can cause side effects like muscle pain or liver issues. Always communicate with your doctor if you experience side effects.
4. Are natural supplements effective for lowering cholesterol?
While some natural supplements, like omega-3 fatty acids and plant sterols, may help lower cholesterol levels, they are not a substitute for prescribed medication. Always consult your doctor before using supplements.
Conclusion
High cholesterol is a serious condition that can lead to heart disease and other complications. While lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are essential in managing cholesterol, some people may need medications to help control their levels. Statins, PCSK9 inhibitors, and other cholesterol-lowering drugs can play a critical role in reducing your risk of cardiovascular disease. If you’re struggling with high cholesterol, consult your doctor to discuss the best treatment plan for you, combining medications and lifestyle changes for optimal heart health.

